Redis is an open-source, in-memory key-value store known for its high performance and versatility. It operates primarily as a cache or a quick-response database, storing data in memory to enable low-latency read and write operations. Redis supports various data structures, including strings, lists, sets, and hashes, making it suitable for a wide range of applications from caching to real-time analytics. Its design allows for rapid data access and manipulation, which is crucial for applications requiring high throughput and low latency.
High Availability Architecture (Sentinel)
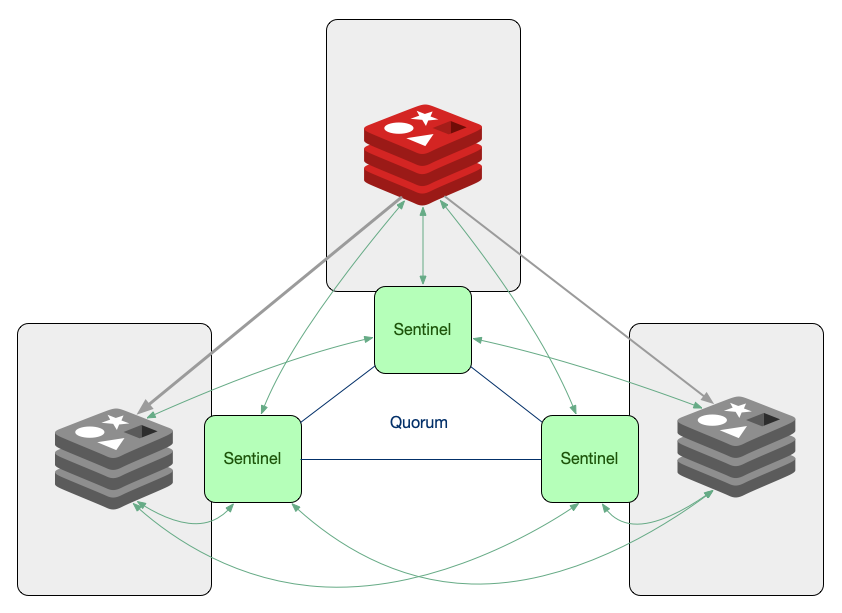
To enhance reliability and availability, Redis can be paired with Redis Sentinel, a system designed to monitor Redis instances and manage failover processes. Sentinel provides automated monitoring of master and slave instances, ensuring that if the master fails, a slave can be promoted to master without manual intervention. This architecture allows applications to maintain continuous operation even in the face of server failures.Key features of Redis Sentinel include:
Monitoring: Sentinel continuously checks the health of master and slave instances.
Automatic Failover: In case of a master failure, Sentinel automatically promotes a slave to become the new master.
Configuration Management: It updates clients with the new master information, allowing them to reconnect seamlessly.
Together, Redis and Sentinel create a robust architecture that ensures high availability and resilience, making it an ideal choice for applications that require constant uptime and reliable data access.
How to Setup
To set up Redis with Sentinel on every machine for high availability, follow these detailed steps. This guide assumes you have three Linux servers ready, each running Redis and Sentinel.
Step 1: Install Redis
On all three servers, install Redis using the following commands:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install redis-server
Step 2: Configure Redis Instances
Server Configuration Overview
- Server 1 (Master, 10.211.11.7) - Runs Redis as the master.
- Server 2 (Replica, 10.211.11.8) - Runs Redis as a replica of Server 1.
- Server 3 (Replica, 10.211.11.9) - Runs Redis as a replica of Server 1.
On Server 1 (Master)
Edit the Redis configuration file located at /etc/redis/redis.conf:
# Allow external connections
bind 0.0.0.0
# Set a password for replication
requirepass your_master_password
# Enable protected mode
protected-mode no
sed -i 's/^bind 127.0.0.1/bind 0.0.0.0/' /etc/redis/redis.conf
sed -i 's/^protected-mode yes/protected-mode no/' /etc/redis/redis.conf
sed -i "s/# requirepass foobared/requirepass <your_password>/" /etc/redis/redis.conf
sed -i -E 's/^#?\s*masterauth.*/masterauth your_password_here/' /etc/redis/redis.conf
# only in replica node
sed -i -E 's/^#?\s*replicaof\s+<masterip>\s+<masterport>/replicaof new_server_ip 6379/' redis.conf
On Server 2 (Replica)
Edit the Redis configuration file on Server 2:
# Allow external connections
bind 0.0.0.0
# Set a password for replication
requirepass your_master_password
# Enable protected mode
protected-mode no
# Configure as a replica of Server 1
replicaof <Server_1_IP> 6379
# Set the master user for replication
masterauth your_master_password
sed -i -E 's/^#?\s*masterauth.*/masterauth your_password_here/' /etc/redis/redis.conf
sed -i -E 's/^#?\s*replicaof\s+<masterip>\s+<masterport>/replicaof new_server_ip new_port/' redis.conf
On Server 3 (Replica)
Repeat the same configuration as on Server 2, but point to Server 1’s IP address.
Step 3: Configure Sentinel on Each Server
Create a Sentinel configuration file on each server. Here’s how to do it:
On All Servers (Sentinel Configuration)
Create a file named sentinel.conf at /etc/redis/sentinel.conf:
port 26379
bind 0.0.0.0
sentinel monitor mymaster <Server_1_IP> 6379 2
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 5000
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 60000
sentinel auth-pass mymaster your_master_password
Make sure to replace <Server_1_IP> with the actual IP address of your master server.
Change permission of file to redis user
chown redis:redis /etc/redis/sentinel.conf
Step 4: Start Redis and Sentinel Services
Start Sentinel Instances
You can start the Sentinel service using the following command on each server:
redis-server /etc/redis/sentinel.conf --sentinel
To run this command in the background, you may want to create a systemd service for Sentinel:
Create a new service file at /etc/systemd/system/redis-sentinel.service:
[Unit]
Description=Redis Sentinel
After=network.target
[Service]
User=redis
Group=redis
Type=simple
ExecStart=/usr/bin/redis-server /etc/redis/sentinel.conf --sentinel
ExecStop=/usr/bin/redis-cli -p 26379 shutdown
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Then enable and start the Sentinel service:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable redis-sentinel.service
sudo systemctl start redis-sentinel.service
Start Redis Instances
On each server, start the Redis service:
sudo systemctl restart redis-server
sudo systemctl enable redis-server
Step 5: Verify Setup
To check if everything is working correctly, connect to one of the Sentinels:
redis-cli -p 26379 SENTINEL masters
This command should return information about the monitored master instance.
Redis client
Sender
import redis
from redis.sentinel import Sentinel
import time
# Define the Sentinel connection details
sentinels = [('10.211.11.7', 26379), ('10.211.11.8', 26379), ('10.211.11.9', 26379)]
password = 'S7WubxPy8ZoPhuTS5bgttw'
def get_master():
"""Get the current master Redis instance from Sentinel."""
while True:
try:
sentinel = Sentinel(sentinels, socket_timeout=0.1)
master = sentinel.master_for('mymaster', password=password)
return master
except (redis.ConnectionError, redis.TimeoutError) as e:
print(f"Error connecting to Sentinel: {e}. Retrying in 5 seconds...")
time.sleep(5) # Wait before retrying
def main():
"""Main function to increment a value in Redis continuously."""
while True: # Run indefinitely until stopped
master = get_master() # Get the master instance
# Log the master node's address
master_address = master.connection_pool.get_connection('SET').host
master_port = master.connection_pool.get_connection('SET').port
print(f"Connected to Redis node at {master_address}:{master_port}")
value = 0 # Initialize the value for INCR
while True: # Continuously attempt to set the value
try:
value += 1 # Increment the value
master.set('INCR', value) # Store the incremented value in Redis under 'INCR'
print(f'Set INCR = {value} in Redis node at {master_address}:{master_port}') # Print confirmation with node info
time.sleep(1) # Sleep for 1 second before next increment
except (redis.ConnectionError, redis.TimeoutError) as e:
print(f"Connection error occurred: {e}. Re-fetching master...")
break # Break to re-fetch master on connection error
# Handle re-fetching of the master after an error
while True:
try:
master = get_master() # Attempt to get a new master
master_address = master.connection_pool.get_connection('SET').host
master_port = master.connection_pool.get_connection('SET').port
print(f"Connected to new Redis node at {master_address}:{master_port}")
break # Exit this loop if successful
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to connect to new master: {e}. Retrying in 5 seconds...")
time.sleep(5) # Wait before retrying
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Receive
import redis
from redis.sentinel import Sentinel
import time
# Define the Sentinel connection details
sentinels = [('10.211.11.7', 26379), ('10.211.11.8', 26379), ('10.211.11.9', 26379)]
password = 'S7WubxPy8ZoPhuTS5bgttw'
def get_master():
"""Get the current master Redis instance from Sentinel."""
while True:
for sentinel_address in sentinels:
try:
sentinel = Sentinel([sentinel_address], socket_timeout=0.1)
master = sentinel.master_for('mymaster', password=password)
return master
except (redis.ConnectionError, redis.TimeoutError) as e:
print(f"Error connecting to Sentinel at {sentinel_address}: {e}. Trying next sentinel...")
time.sleep(1) # Short wait before trying next sentinel
print("All sentinels are unreachable. Retrying in 5 seconds...")
time.sleep(5) # Wait before retrying all sentinels
def main():
while True: # Run indefinitely until stopped
master = get_master() # Get the master instance
# Get the master node's address for logging
master_address = master.connection_pool.get_connection('GET').host
master_port = master.connection_pool.get_connection('GET').port
print(f"Connected to Redis node at {master_address}:{master_port}")
while True: # Run indefinitely until stopped
try:
# Fetch the value of the 'INCR' key from Redis
value = master.get('INCR')
# Decode the value if it is not None
if value is not None:
value = int(value)
print(f'Retrieved INCR = {value} from Redis node at {master_address}:{master_port}')
time.sleep(1) # Sleep for 1 second before the next iteration
except (redis.ConnectionError, redis.TimeoutError) as e:
print(f"Connection error occurred: {e}. Re-fetching master...")
break # Break to re-fetch master on connection error
# Handle re-fetching of the master after an error
while True:
try:
master = get_master() # Attempt to get a new master
master_address = master.connection_pool.get_connection('GET').host
master_port = master.connection_pool.get_connection('GET').port
print(f"Connected to new Redis node at {master_address}:{master_port}")
break # Exit this loop if successful
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to connect to new master: {e}. Retrying all sentinels in 5 seconds...")
time.sleep(5) # Wait before retrying
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Conclusion
With this setup, each server runs both a Redis instance and a Sentinel instance, providing high availability through monitoring and automatic failover capabilities. This configuration allows for redundancy and ensures that if one server goes down, others can take over seamlessly. Always ensure that your passwords are strong and consider additional security measures based on your environment’s needs.
Citations:
- [1] https://redis.io/learn/operate/redis-at-scale/high-availability/exercise-2
- [2] https://redis.io/docs/latest/operate/oss_and_stack/management/sentinel/
- [3] https://docs.servicestack.net/redis/sentinel
- [4] https://facsiaginsa.com/redis/setup-redis-ha-using-sentinel
- [5] https://dev.to/hedgehog/set-up-a-redis-sentinel-3m50
- [6] https://github.com/ServiceStack/redis-config
- [7] https://stackoverflow.com/questions/53284461/redis-sentinel-with-only-one-host
